The internet has come a long way since its early days of static web pages. With the advent of social media and user-generated content, the web has evolved into a dynamic and interactive platform. However, concerns about the manipulation of user data by centralized institutions have emerged. Web3, the next evolution of the web, promises to address these issues while revolutionizing the way we access information and services.
But what are the risks associated with Web3? In this article, we will explore the potential security vulnerabilities of the Web3 ecosystem and their impact on the broader web. Understanding these risks is crucial for the successful adoption of Web3 technologies.
Contents
Why Does Web 3.0 Matter?
Before delving into the risks, let’s understand why Web3 is so important. Web3 introduces the concept of the “semantic web,” where all data on the web becomes machine-readable. This means that computers can better understand the meaning of web elements, leading to contextually appropriate search results with greater accuracy.
Web3 also emphasizes decentralization, which prevents the undue influence of big tech companies on internet access and gives users control over their own data without intermediaries. It promises a deeper contextual understanding of web pages and facilitates better information analytics and transactions.
What are the Risks for Web3?
While Web3 offers exciting possibilities, it also comes with its share of risks. One of the main challenges is the lack of a centralized framework for verifying information added to the web. Without gatekeepers, anyone can contribute content, potentially leading to misinformation and unverified data.
Additionally, the machine-readable nature of Web3 data makes it vulnerable during transit, as it can be interpreted by both people and machines. Users also bear the responsibility of securing their data, which opens up concerns about data manipulation, confidentiality, information quality, and data availability.
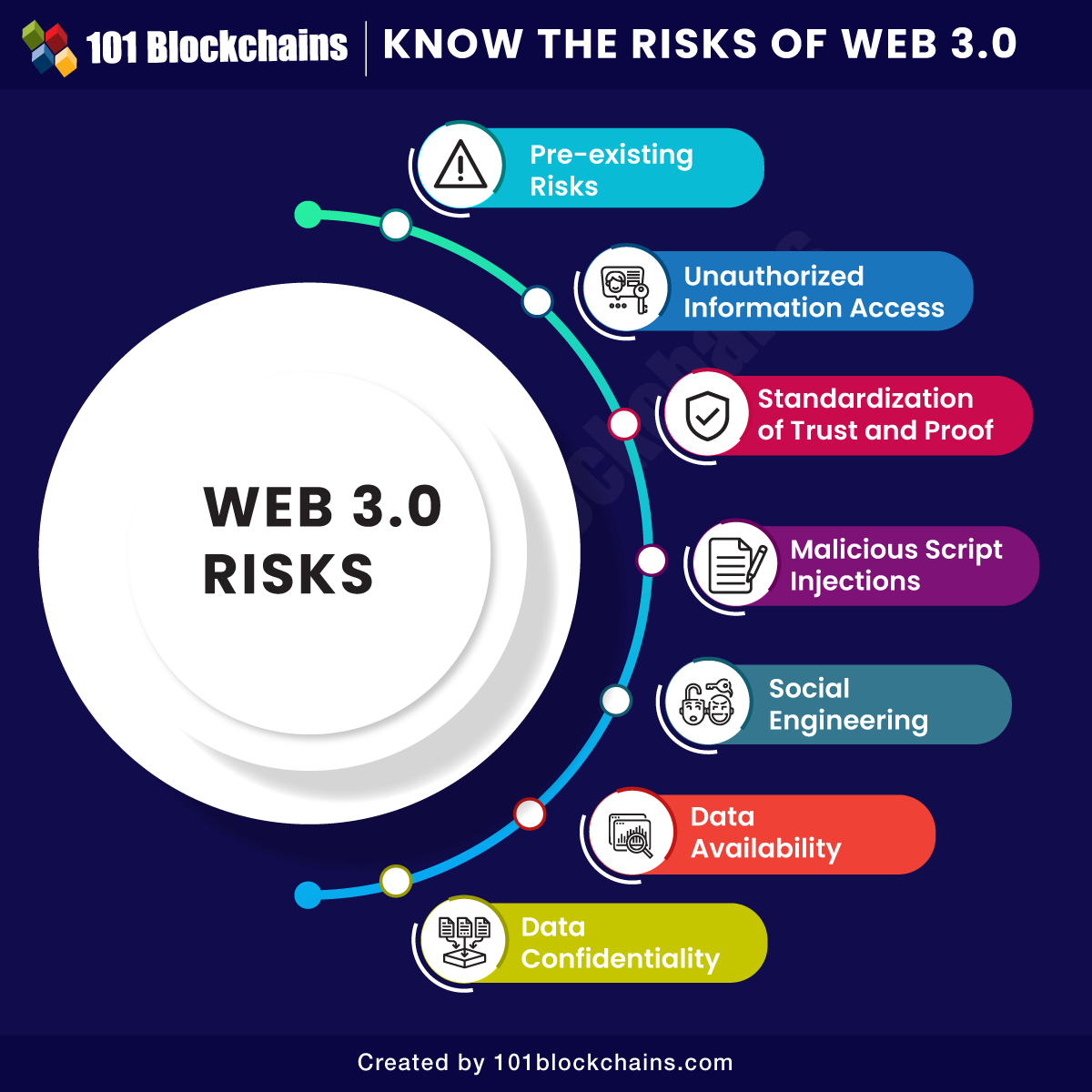
Pre-existing Risks
Web3 inherits some security vulnerabilities from previous generations of the internet. These include potential loss of confidential information, unauthorized digital intrusion, non-compliance with regulations, dependence on third-party services, performance setbacks due to continuous updates, limited experienced staff, and wasteful resource utilization.
One of the primary risks in Web3 is unauthorized access to sensitive information. As the amount of data on the web grows exponentially, hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the system. Unauthorized access, data manipulation, network eavesdropping, and message relay attacks are some examples of how sensitive information can be compromised.
Standardization of Trust and Proof
In Web3, establishing trust becomes crucial due to the autonomous harvesting and integration of data. Users must verify the source and policies of information to determine its trustworthiness. Malicious agents can create scripts or manipulate ranking algorithms to deceive users, leading to unsafe transactions or exposure to dangerous scripts and malware.
Malicious Script Injections
Web3 relies on various programming languages, and vulnerabilities can arise in query or update languages. Script injections, such as SPARQL injections, can allow unauthorized access and manipulation of the back-end layer of databases. These script injections enable attackers to extract sensitive information and even write malicious scripts, compromising the security of web3 applications.
Social Engineering
Web3 introduces semantic metadata and ontologies for better integration capabilities, but this also exposes users to social engineering attacks. Hackers can employ inference attacks to mine sensitive information or assume the identity of trusted third parties. Identity theft is another concern, as sensitive metadata information can be exploited by scriptwriters.
Data Availability
With the increasing digitalization of everything, data availability becomes a significant concern in Web3. Broken links and unpredictable data sources can disrupt web3 systems, making IT teams lose control over the availability of data.
Data Confidentiality
Web3 brings enhanced semantic capabilities, making data more readable and understandable. However, this also increases the risk of interception and exposure of sensitive information. Confidentiality breaches can occur if data is inadvertently stored in insecure locations or if web3 systems lack adequate encryption and security measures.
Final Words
While Web3 holds immense potential, it is essential to address the associated risks for a smooth transition. Security challenges, such as unauthorized access, data confidentiality, and information quality, can impact the adoption of web3 technologies. Recognizing these risks and taking a proactive approach to address them is crucial to ensure the successful implementation of web3. To learn more about the risks associated with the web3 ecosystem, visit Virtual Tech Vision.







