
The solar industry in the United States is experiencing unprecedented growth, fueled by factors such as declining costs, increasing demand for clean electricity, and strong federal policies like the solar Investment Tax Credit. The Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), in collaboration with Wood Mackenzie Power & Renewables, has been diligently tracking the trends and trajectories in the solar industry, offering valuable insights into its diverse and sustained growth across the country.
Contents
- 1 Massive Growth Sets the Stage for the Solar+ Decade
- 2 Solar as an Economic Engine
- 3 Growth Driven by Falling Prices
- 4 Recent Challenges and Opportunities
- 5 Solar’s Growing Share of New Capacity
- 6 Diversification of State Markets
- 7 Challenges in Residential Market
- 8 Emerging Commercial Markets and the IRA
- 9 Solar PV Growth Forecast
- 10 The Role of the Inflation Reduction Act
- 11 Securing the Supply Chain through Manufacturing
- 12 Towards Aggressive Growth and Climate Goals
- 13 Solar Means Business
- 14 Conclusion
Massive Growth Sets the Stage for the Solar+ Decade
Over the past decade, solar energy has witnessed an impressive average annual growth rate of 22%. As a result, the nation now boasts over 179 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity, enough to power nearly 33 million homes. This exponential growth can be attributed to a combination of favorable federal policies, considerable cost reductions, and a surge in demand for clean energy by both private and public sectors.
Solar as an Economic Engine
The solar industry is not only transforming the energy landscape but also making a significant impact on the economy. As of 2022, more than 263,000 Americans are employed in the solar sector across more than 10,000 companies, spanning every state in the nation. In 2023 alone, the industry generated nearly $51 billion in private investments, providing a substantial boost to the American economy.
Growth Driven by Falling Prices
The cost of solar installation has witnessed a remarkable drop of over 40% in the last decade. This decline in prices has led to the expansion of the industry into new markets, with thousands of solar systems being deployed nationwide. For instance, the cost of an average-sized residential system has gone down from $40,000 in 2010 to approximately $25,000 today. Moreover, utility-scale solar prices now range from $16/MWh to $35/MWh, making them highly competitive with other forms of energy generation.
Recent Challenges and Opportunities
While solar pricing has experienced volatility in the past few years, with inflation and supply chain constraints affecting prices, the situation is gradually improving. As more solar modules become available and domestic manufacturing capacity increases, prices are being driven downward. This was evident in Q4 2023 when an oversupply of modules led to a significant decline of 25% to 35% in total system prices.
Solar power has emerged as the leading source of new generating capacity in the United States for five consecutive years. In 2023, solar accounted for a remarkable 53% of all new electric capacity added to the grid, marking the first time in 80 years that a renewable energy resource captured the majority share. Solar’s increasing competitiveness against other technologies has propelled its share of total U.S. electrical generation from a mere 0.1% in 2010 to over 5% today.
Diversification of State Markets
While California has traditionally dominated the U.S. solar market, other states are quickly catching up. Texas, Florida, and Ohio, amongst others, experienced significant growth in 2023. Furthermore, the number of U.S. states with 1 GW or more of installed solar capacity has risen from just three a decade ago to half of all states today. As solar demand continues to rise, new entrants will command a larger share of the national market.
Challenges in Residential Market
The residential solar market achieved a record-breaking year in 2023, with nearly 7 GW of installations. This growth was driven by high household electricity bills, power outages, and changes in California’s Net Metering rules. However, a contraction is expected in the residential market in 2024 due to the completion of the California queue and higher financing costs in other markets.
Emerging Commercial Markets and the IRA
The commercial solar market, historically dominated by a few states, is poised for growth in emerging markets due to the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). The IRA’s provisions, such as transferability, direct pay, and adder credits, are expected to drive expansion in commercial solar. The market for community solar installations is also diversifying as more states and utilities create and expand community solar programs, making solar energy accessible to a wider range of households and businesses.
Solar PV Growth Forecast
Despite supply chain challenges in 2022, the solar industry bounced back in 2023 and deployed a record-breaking 32.4 GW of solar capacity. The industry’s total solar fleet is projected to quadruple over the next decade, reaching 673 GW, as the Inflation Reduction Act provides key tax incentives and long-term certainty that will drive demand for solar and storage, accelerating the transition to renewable energy.
The Role of the Inflation Reduction Act
The passage of the Inflation Reduction Act has significantly improved the outlook for the solar industry in the next five years. The long-term tax incentives and manufacturing provisions contained in the IRA are projected to increase expected solar deployment by 38% compared to pre-IRA projections. However, the industry awaits further guidance from the Biden Administration on specific provisions of the law, which will have far-reaching implications for future growth potential.
Securing the Supply Chain through Manufacturing
In addition to driving massive deployment of solar energy, the IRA is expected to revive U.S. solar manufacturing. Over 100 GW of solar module manufacturing capacity has been announced since the beginning of 2022, along with numerous facilities producing other components of the supply chain. This development will enhance supply chain reliability, create jobs, and stimulate investment in clean energy. Moreover, significant investment has been made in battery storage manufacturing to ensure a reliable domestic supply for the solar and storage industries.
Towards Aggressive Growth and Climate Goals
While the current growth trajectory puts the solar market within reach of ambitious clean energy goals set by the industry and the Biden administration, more aggressive efforts are required. Annual installations must increase from less than 22 GW in 2022 to nearly 140 GW by 2030, with cumulative totals exceeding 800 GW by the end of the decade. Achieving these targets will necessitate a combination of private sector innovation and stable, long-term public policies that will help address climate change and decarbonize the economy.
Solar Means Business
The commitment to solar energy extends beyond households and governments, with major U.S. corporations recognizing its benefits. Companies like Meta, Amazon, Apple, Walmart, and Microsoft are leading the way by investing heavily in solar and renewable energy. As of June 30, 2022, these top corporate solar users have installed nearly 19 GW of solar capacity across a vast network of almost 50,000 facilities throughout the country. This demonstrates the growing role of solar in helping Fortune 500 companies save money and reduce their environmental footprint.
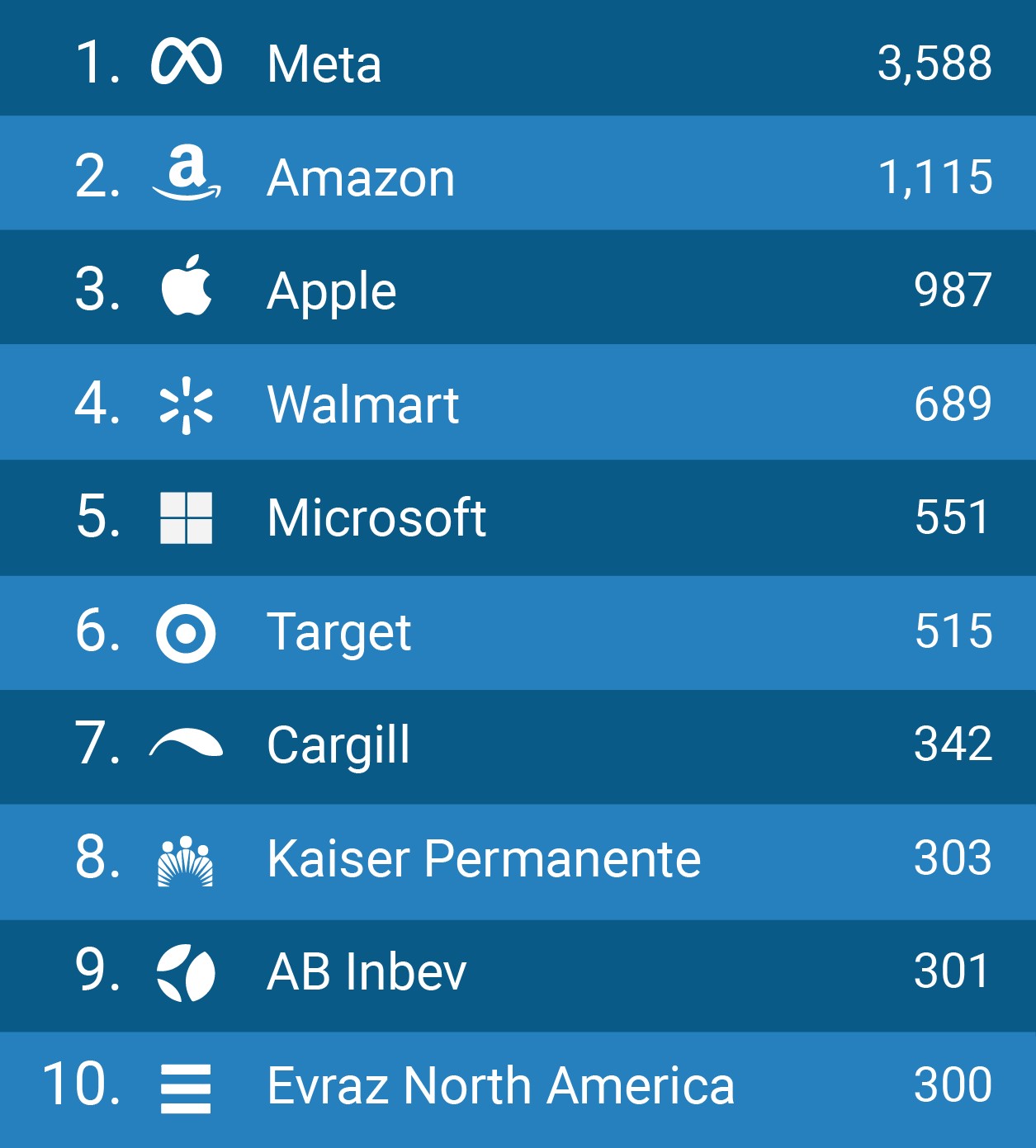
For more information on corporate solar adoption and to explore SEIA’s Solar Means Business report, including interactive maps and data tools, visit Virtual Tech Vision.
Conclusion
The solar industry in the United States is experiencing tremendous growth, driven by factors such as declining costs, increasing demand, and supportive federal policies. With the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act, the solar market is expected to flourish even further, aided by tax incentives and manufacturing provisions. However, to achieve ambitious clean energy goals and combat climate change, the industry must strive for more aggressive growth and innovation. By continuing to embrace solar energy, the United States can pave the way for a sustainable and decarbonized future.







